Capital Gains Tax Guide UK 2025
Everything You Need to Know
Capital Gains Tax (CGT) remains one of the most important considerations for UK investors in 2025. With the government tightening tax allowances and more people facing unexpected tax bills, understanding how Capital Gains Tax UK works has never been more crucial. Whether you invest in shares, property, or other assets, CGT can impact your returns significantly if you don’t plan ahead.
What Is Capital Gains Tax UK?
Capital Gains Tax is the tax you pay on the profit (or gain) when you sell or dispose of an asset that has increased in value. It applies to a wide range of assets, including:
- Shares, ETFs, and investment funds
- Second homes and buy-to-let property
- Certain personal possessions over £6,000 (e.g. art, antiques)
- Business assets
The key point is that you are taxed only on the profit, not the entire value of the sale.
Example: If you bought shares for £5,000 and later sold them for £12,000, your gain is £7,000. That £7,000 is potentially subject to Capital Gains Tax UK, depending on your allowance and tax band.
CGT Allowance UK 2025
The UK government has significantly reduced the Capital Gains Tax (CGT) allowance in recent years. For the 2025/26 tax year, this allowance stands at a mere £3,000 per person. While couples can combine their allowances for a total of £6,000, this represents a substantial decrease from the £6,000 individual allowance in 2023/24.
In simpler terms, if your investment profits (capital gains) for the year are below £3,000, you won't pay any CGT. However, any gains exceeding this threshold will be subject to CGT. This lower allowance makes careful financial planning crucial, particularly for those with substantial investment portfolios. It's now more important than ever to consider tax-efficient investment strategies to minimise your tax liability.
Capital Gains Tax Rate UK 2025
Here's a breakdown for 2025 (please note that tax rates can change, so always verify with official government sources before making financial decisions):
For Shares and Other Investments
- Basic-rate taxpayers: Will pay CGT at a rate of 10% on their profits.
- Higher- and additional-rate taxpayers: Will pay CGT at a rate of 20% on their profits.
For Residential Property (excluding your main home)
- Basic-rate taxpayers: Will pay CGT at a rate of 18% on their profits.
- Higher- and additional-rate taxpayers: Will pay CGT at a rate of 24% on their profits.

How to Calculate Capital Gains Tax UK
Calculating your UK Capital Gains Tax (CGT) can seem complex, but breaking it down step-by-step makes it manageable.
Calculate Your Gain
This is the profit you made from selling an asset. It’s the difference between:
- Sale price: The amount you received when you sold the asset.
- Purchase price: The original cost of the asset.
- Allowable costs: Expenses directly related to buying and selling the asset. This includes things like broker fees, legal fees, and stamp duty (if applicable). Keep thorough records of these costs!
EXAMPLE
You bought shares for £10,000, paid £100 in broker fees, and sold them for £15,000.
Your net gain is £4,900, i.e.,
£15,000(sale price) – £10,000 (purchase price) – £100 (broker fees) = £4,900.

Apply Your Annual Exempt Amount
The UK government provides an annual Capital Gains Tax allowance. This is the amount of capital gains you can make each tax year without paying any CGT. For the 2023/24 tax year, this allowance is £6,000. This amount is subject to change, so always check the latest HMRC guidance.
As in above example, your gain of £4,900 which is less than the £6,000 allowance, so you don’t owe any CGT.
If Your Gain Exceeds the Allowance
If your gain is more than your annual exempt amount, you’ll need to pay CGT on the excess. The rate depends on your total income, including the capital gain:
- 10%: Applies to gains from the sale of residential property if your total income (including the gain) is within the basic rate income tax band.
- 18%: Applies to gains from the sale of residential property if your total income (including the gain) is within the higher rate income tax band.
- 20%: Applies to most other assets if your total income (including the gain) is within the basic rate income tax band.
- 28%: Applies to most other assets if your total income (including the gain) is within the higher rate income tax band.
SHARE EXAMPLE
Let’s say your gain was £10,000, and your total income is within the basic rate band.
You’d pay CGT on £10,000 – £3,000 (allowance) = £7,000.
The CGT rate for most assets in the basic rate band is 20%, so your CGT liability would be £7,000 * 0.20 = £1,400.

PROPERTY EXAMPLE
You bought a second home for £200,000, and sold it for £260,000, so the total gain is of £60,000.
Now, deduct £3,000 CGT allowance, which gives you the total taxable gain, £57,000.
Let’s consider you’re a higher-rate taxpayer, then the total CGT you need to pay is: £57,000 × 24% = £13,680.

Exemptions from Capital Gains Tax UK
Several exemptions exist, meaning you won't pay CGT on certain gains. These includes
Your main home (Private Residence Relief)
Generally, you won't pay CGT on profits from selling your primary residence. There are specific rules and conditions around this, particularly concerning periods of ownership and any parts of the property used for business purposes.
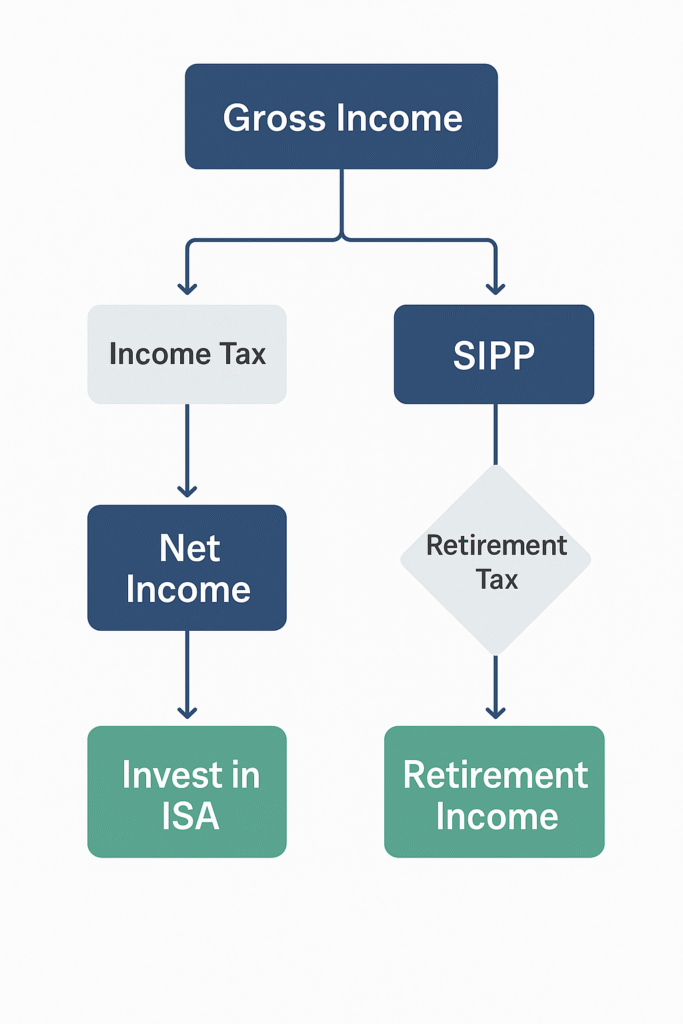
ISAs (Individual Savings Accounts)
Gains made within an ISA are tax-free. This is a key benefit of using ISAs for saving and investing.
Pensions (SIPPs and workplace pensions)
Withdrawals from pension schemes, including Self-Invested Personal Pensions (SIPPs) and workplace pensions, are generally not subject to CGT. However, income tax may apply to the withdrawals.
Premium Bonds and lottery winnings
These are considered exempt from CGT as they are not considered investments in the traditional sense.
Transfers between spouses or civil partners
Transferring assets between spouses or civil partners during marriage or civil partnership is generally exempt from CGT.
It’s crucial to remember that these are simplified explanations. The specific rules and conditions surrounding each exemption can be complex. For detailed information and to ensure you understand how these exemptions apply to your individual circumstances, it’s advisable to consult the official HMRC guidance or seek professional financial advice.
How to Reduce Capital Gains Tax UK
Minimising your Capital Gains Tax (CGT) liability in the UK is crucial, especially given the recent reduction in the annual exempt amount. Here's a breakdown of common strategies, explained in plain English, to help you protect your investment returns:
The Bed and ISA Strategy
This involves selling assets outside your ISA, realising capital gains up to your annual allowance. Immediately afterwards, repurchase the identical assets within your ISA. Any future growth on these assets will then be completely tax-free. Think of it as “bedding down” your gains within the safe haven of your ISA.
Gifting to Your Spouse
Transferring assets to your spouse is a powerful tax-planning tool. This transfer doesn’t trigger CGT. Effectively, this doubles your household CGT allowance, allowing you to spread gains across potentially lower tax bands. Remember to consider the implications for inheritance tax in the long term.
Tax-Loss Harvesting
If you’ve experienced losses on some investments, you can use them to offset gains. Sell assets that are currently showing a loss within the same tax year as you realise gains. This reduces your overall taxable gains. Any unused losses can even be carried forward to offset future gains.
Maximise Pension Contributions
Investing in a pension (either a Self-Invested Personal Pension – SIPP – or your workplace pension) offers a significant CGT advantage. Gains within a pension are completely tax-free. Furthermore, contributions often attract tax relief, meaning the government effectively contributes towards your pension savings.
Staggering Asset Sales
Don’t rush into selling all your assets at once. Spread your sales over multiple tax years to make the most of your annual CGT allowance each year. This allows you to utilise the full allowance without exceeding it and incurring unnecessary tax.
Capital Gains Tax UK for Property Investors
Capital Gains Tax (CGT) in the UK significantly impacts property investors, particularly landlords. Recent changes have drastically reduced the annual CGT allowance, meaning many landlords selling buy-to-let properties now face substantially higher tax bills. It's crucial to remember that any capital gains from property sales in the UK must be reported and the tax paid within 60 days of the completion of the sale. Failure to meet this deadline will incur penalties and interest charges. This highlights the importance of careful financial planning and timely tax reporting for property investors.
Reporting and Paying Capital Gains Tax UK
In the UK, you'll need to report and pay Capital Gains Tax (CGT) on profits from selling assets like property or shares. There are two main ways to do this:
- Self Assessment tax return: This is the usual method for most CGT liabilities. You’ll declare your capital gains alongside your other income on your annual Self Assessment tax return. This is submitted online through the HMRC website.
- HMRC’s Capital Gains Tax service: For property sales specifically, you might be able to use HMRC’s dedicated online service. This streamlines the process for reporting property gains. Check HMRC’s website for eligibility.
Crucially, meticulous record-keeping is essential. HMRC may ask for proof to support your CGT calculation. This means keeping detailed records of:
- Purchase price: The original cost of the asset.
- Costs of acquisition: Any fees or expenses incurred when buying the asset (e.g., solicitor’s fees, stamp duty).
- Costs of disposal: Expenses related to selling the asset (e.g., estate agent fees).
- Receipts and supporting documentation: Keep all relevant paperwork to verify your claims.
Failing to keep accurate records can lead to delays and penalties. It’s advisable to consult a tax professional if you’re unsure about any aspect of reporting and paying your CGT. They can help ensure compliance and potentially identify ways to minimise your tax liability within the legal framework.
Important Considerations
- Different asset types: The rules can vary slightly depending on the type of asset you’re selling (shares, property, etc.).
- HMRC guidance: Always refer to the official HMRC website for the most up-to-date information and specific guidance relevant to your situation. This information is for guidance only and doesn’t constitute financial advice.
- Professional advice: If you’re unsure about any aspect of calculating your CGT, it’s best to seek advice from a qualified accountant or financial advisor.
Remember to keep accurate records of all your transactions to ensure you calculate your CGT correctly. Failing to do so could lead to penalties.



Use ISA
Save for a house deposit in 5 years